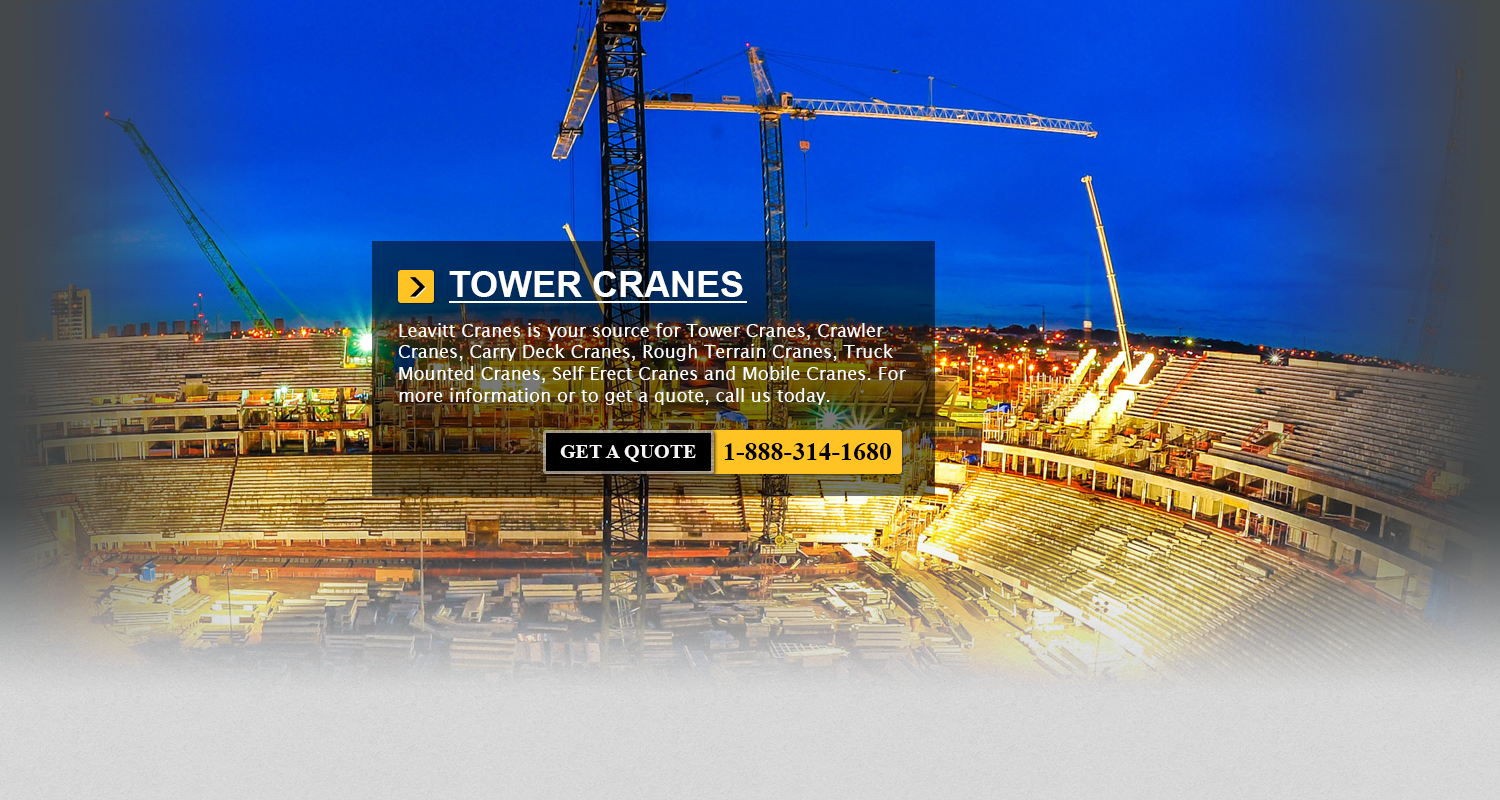
JCB Aerial Lifts Salem
Aerial Work Platforms
The AWP or aerial work platform is a machinery designed and engineered to raise employees and gear to a particular height for the completion of tasks. The kind of machine varies with the particular brand and unit. Before aerial work platforms were developed, all tasks which need work at high levels needed to be carried out with scaffolding. Therefore, the invention of aerial work platforms has kept a lot of employees safe and increased the overall productivity of similar jobs.
There are 3 key kinds of aerial work platforms. They are scissor lifts, boomlifts and mechanical lifts. These machinery are able to be operated with pneumatics, mechanically utilizing a rack and pinion system or by hydraulics or with screws. These units may be self-propelled with controls situated at the platform, they may be unpowered units needing an external force to move them or be mounted to a vehicle so as to be transported.
John L. Grove was an American inventor and industrialist who is widely credited to devising the aerial work platform. Nevertheless, during 1966, before the first model of JLG, a company called Selma Manlift introduced an aerial lift unit.
In the year 1967, after selling his previous business Grove Manufacturing, John L. Grove together with his wife decided to take a road trip. They decided to stop at Hoover Dam. While the couple was there, Grove unfortunately witnessed 2 employees electrocuted while they were working on scaffolding. This terrible event led John Grove to discover an untapped market for a new product that could raise employees safely in the air for them to perform construction and maintenance tasks in a better way.
Once John returned home from his vacation, he bought a small metal fabrication company and formed a partnership along with 2 friends. They immediately started designing ideas for the aerial work platform. The new business was named JLG Industries Inc. They proudly launched their first aerial work platform in the year 1920 with the aid of 20 workers.
- Caterpillar IC Forklifts Salem
In order to help you select the right Forklift Tire and Compound, we would ask you to think about the following things: kind of fuel utilized; weight of your standard load; typical length of your... More - Daewoo Counterbalance Forklifts Salem
Using a Regular Counterbalance lift truck 1 Perform a pre-shift check before operating the equipment. Occupational Safety and Health Administration guidelines state that a pre-shift checklist must be performed at the start of every work... More - Nissan Electric Forklifts Salem
Usually, electric forklifts are the best choice for indoor use in warehouses and manufacturing applications for 2 major reasons: First off they produce zero emissions. This is an extremely vital factor to take into account... More - Hyster Narrow Aisle Forklifts Salem
Hyster has a new ergonomically correct order picker which highlights an exceptional work station for the driver. It has a spacious platform, an anti-fatigue floor mat, a multi-function control handle and fixed-hoop rails. This kind... More - Liebherr Construction Cranes Salem
The Liebherr family business was created during the year 1949 by Hans Liebherr. The business first gained fame from its mobile tower crane which was well-known for its ease of assembly and affordability. It was... More